Fiber Optic is a type of cable made of glass or very fine plastic, fiber optic cable can transmit light signals from one location to another at high speed using light refraction as its working principle. The light source used is a laser or LED. Fiber optics have become a major component of the telecommunications world.
Optical fiber has a unique working principle, because it does not use an electric current, but instead uses a stream of light that is converted from an electric current so that it will not be disturbed by electromagnetic waves. The constituent material is glass fiber which is useful for getting high light reflection from the mirror so that the data will be transmitted quickly at an unlimited distance.
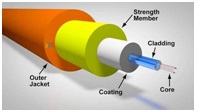
Fiber optic cable components include:
- Core part (Core)
The core of optical fiber is made of glass material with a very small diameter (diameter about 2 μm to 50 μm). A larger diameter optical fiber will make performance better and more stable. - Cladding Section Cladding
section is a protective part that directly covers the optical fiber. Usually the size of this cladding is 5 μm in diameter to 250 μm. Cladding is made of silicon, and the composition of the material is different from the core. In addition to protecting the core, cladding also functions as a guide to light waves that reflect all translucent light back to the core. - Coating / Buffer
Section The coating section is a coat of different optical fibers from cladding and cores. This coating layer is made of elastic plastic material. Coating serves as a protective layer from all physical disturbances that may occur, such as curvature of the cable, humidity in the cable. - Strength Member & Outer Jacket Section
This layer is a very important part because it is the main protector of a fiber optic cable. The strength member and outer jacket layers are the outer portion of the optical fiber that protects the cable core from various physical interference directly.
The advantages of fiber optic cables include:
- High transmission speed (1GB / s) and can reach long distances
- Rust resistant
- Cable size is small and flexible
- Not disturbed by electromagnetic waves and radio
- Prevents short circuit because it does not contain electricity
- Minimal distortion
With the advantages above, optical fiber is superior to other cables. So it is not strange if this cable is the main choice for large network users and requires a high speed rate.
Comments
Post a Comment